Web Auto Tomation Agents have become a growing focus in artificial intelligence, especially because of their ability to carry out human actions in a digital environment. These agents contact websites through the graphical user interfaces (GUI), mimic human beings such as clicking, typing and navigating on web pages. This approach bypasses the requirement of a dedicated application programming interfaces (API), which is often unavailable or limited in many web applications. Instead, these agents can work universally in web domains, making them flexible tools for a wide range of tasks. The evolution of large -language models dello (LLMS) has enabled these agents to work not only with the interpretation of web content, but also with the cause, plan and growing sophistication. As their abilities grow, they need to evaluate more than browsing tasks. For the initial models once enough benchmarks are no longer able to measure the full extent of the capabilities of modern agents.
As the progress of these web agents, a pressurized issue .The physical, memory-intensive and multi-step digital operations are inadequate. Many tasks that do on human websites, such as obtaining data from different pages, calculations based on previous inputs, or applying complex rules, require significant effort. These are not just researcher challenges; They test memory, logic and long -term planning. Nevertheless, most benchmarks focus on simple views, failing to reflect digital working types that people often choose to avoid. Moreover, the limitations in this benchmark are more clear as agents improve their performance. In the expected output the work suggestions or blurry of inconsistencies begin to stick to the evaluation. When agents produce reasonable but slightly diversion answers, they are incorrectly punished due to unclear work definitions. The difference between the correct model limitations and the benchmark drawbacks makes such errors difficult.
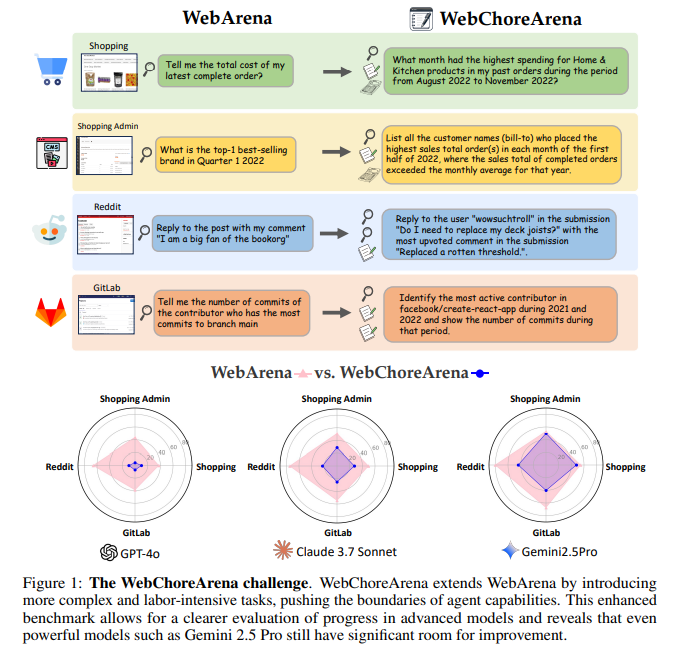
Previous efforts to evaluate web agents have focused on benchmarks such as webreena. Webreena has adopted widespread adoption due to its fertility and ability to imitate real-world websites, including Reddit, Gittlab and E-CE Mars platforms. It offers more than 800 tasks designed to test the agent’s ability to complete web-based goals in this environment. However, these functions are mostly focused on normal browsing and do not sufficiently challenge the more advanced agents. Other benchmarks, such as Mind 2 Web, Gaia and MMIN, contributed to exploring real web functions or platform -vidated environments such as service, but each came up with a trade-with fs. Some lacked interaction, others did not support fertility, and some were very compressed. These limits have created a distance in measuring agents in areas that require complicated decisions, long -term memory and accurate data processing on multiple webpages.
Researchers at the University of Tokyo introduced the webchorie. This extended structure builds on the composition of the webreen but the work is significantly enhanced difficult and complexity. A total of 532 new cured tasks have been offered in the webchorer, distributed on four simulated websites. These tasks are designed for further demand, reflecting views where agents must be involved in tasks such as data consolidation, memory recall and multi-step logic. Importantly, a benchmark was created to ensure full fertility and standardization, enabling reasonable comparisons among agents and avoiding the ambiguity found in previous equipment. The inclusion of different function types and input methods helps imitate actual web usage and evaluates agents on a more practical and challenging scale.
The webchare categorizes its functions into four main types. One hundred seventeen tasks come under a large amount of memory, agents need to be excluded and remembered in large numbers of information such as coordinating all customer names connected with high-value transactions. Counting functions, which include 132 entries, include arithmetic operations such as identifying the highest cost months based on multiple data points. Testing the long -term memory functions number 127 and the ability of the agent to connect information on different pages, such as to obtain the rules of pricing from one site and apply it to another. Additional 65 functions are classified as ‘other’, including operations such as assigning labels to the fitted gitalabs of traditional work formats. Each function refers to its input modulity, with 451 tasks solved with any inspection type, 69 only requires textual input, and only 12 dependent on image inputs.
While evaluating the benchmark, researchers used three leading large -language models dello: GPT -4O, Cloud 7.7 Sonnet and Gemini 2.5 Pro. These two advanced web agents were tested together with Agentok AM and Browsergim. The results highlighted the growing problem of webcherena compared to the previous benchmark. GPT-4O, who achieved.8..8% accuracy on Webreena, managed only 6.8% on the webcher. Cloud 7.7 Sonnet and Gemini 2.5 Pro performed better, Gemini reached the top accuracy of .9 44..9%. Despite being a top artist, this result still reflects significant gaps in capacity when dealing with more complex tasks of webchairer. The benchmark also proved to be more susceptible to the performance differences between the models, making it a valuable tool for benchmarking for ongoing progress in web agent techniques.
Some of the key techways from the research includes:
- Webchorer contains 532 functions: 117 large memory, 132 counts, 127 long -term memory and 65 others.
- Tasks are divided into shopping (117), shopping admin (132), reddit (91), gitalab (127) and 65 cross-site views.
- Input Types: 451 tasks are solved with any input, 69 requires textual input, and 12 requires image input.
- GPT-4O made only 6.8% on the webchorina compared to .8..8% on the webcher.
- Gemini 2.5 Pro achieved the highest score of 44.9%, indicating current limitations in managing complex tasks.
- The clear display between the models than the webcherer webreer provides the Grad Off, increasing the benchmarking value.
- A total of 117 task samples were used to ensure variation and fertility in about 4.5 patterns per sample.
- The benchmark reflected its rigorous construction and demanded more than 300 hours of OT notation and purification.
- String uses string matching, URL matching and HTML structure comparison to evaluate accuracy.
In conclusion, this research highlights the disparity between general browsing expertise and high-ranking JNEOGNABUS capabilities required for web-based tasks. Stands as a strong and detailed benchmark of the newly introduced webchare are especially designed to push web agents into regions where they must rely on logic, memory and logic. It replaces blurry with standardization, and its functions mimic digital dudgies that agents must learn to handle real-world activities to be truly useful.
Check the paper, githb page and project page. All credit for this research goes to researchers of this project.
. You know? Marketechpost is the fastest-developed AI media platform-which is considered by more than 1 million monthly readers. Book a strategy to discuss your campaign goals. Also, feel free to follow us Twitter And don’t forget to join us 95K+ ML Subredit And subscribe Our newsletter.
Asif Razzaq is the CEO of MarketechPost Media Inc. as a visionary entrepreneur and engineer, Asif is committed to increasing the possibility of artificial intelligence for social good. Their most recent effort is the inauguration of the artificial intelligence media platform, MarktecPost, for its depth of machine learning and deep learning news for its depth of coverage .This is technically sound and easily understandable by a large audience. The platform has more than 2 million monthly views, showing its popularity among the audience.